Element Mass Matrix¶
We have
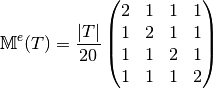
Then with 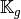 definition (see Section New Optimized assembly algorithm (OptV2 version)) , we obtain
definition (see Section New Optimized assembly algorithm (OptV2 version)) , we obtain
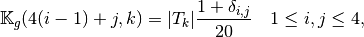
So the vectorized algorithm for 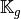 computation is simple and given in Algorithm 27.
computation is simple and given in Algorithm 27.
Algorithm 27
Note
- pyOptFEM.FEM3D.elemMatrixVec.ElemMassMat3DP1Vec(nme, volumes)[source]
Computes all the element Mass matrices
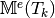 for
for 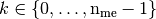
Parameters: volumes ( 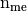 numpy array of floats) – volumes of all the mesh elements.
numpy array of floats) – volumes of all the mesh elements.Returns: a one dimensional numpy array of size 
Element Stiffness Matrix¶
We have 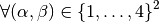
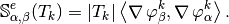
Using vectorized algorithm function 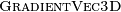 given in Algorithm 26, we obtain
the vectorized algorithm 28 for
given in Algorithm 26, we obtain
the vectorized algorithm 28 for 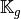 computation for the Stiffness matrix in 3d.
computation for the Stiffness matrix in 3d.
Algorithm 28
Note
- pyOptFEM.FEM3D.elemMatrixVec.ElemStiffMat3DP1Vec(nme, q, me, volumes)[source]
Computes all the element stiffness matrices
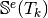 for
for 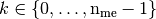
Parameters: - nme (int) – number of mesh elements,
- q (
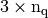 numpy array of floats) – mesh vertices,
numpy array of floats) – mesh vertices, - me (
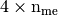 numpy array of integers) – mesh connectivity,
numpy array of integers) – mesh connectivity, - areas (
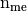 numpy array of floats) – areas of all the mesh elements.
numpy array of floats) – areas of all the mesh elements.
Returns: a one dimensional numpy array of size
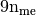
Element Elastic Stiffness Matrix¶
We define on the tetrahedron
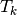 the local alternate basis
the local alternate basis 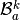 by
by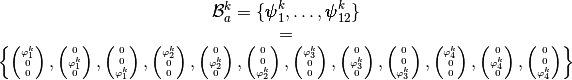
where
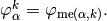 With notations of Presentation,
we have
With notations of Presentation,
we have 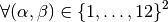
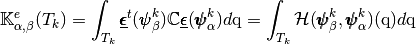
with,
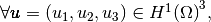
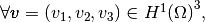 by
by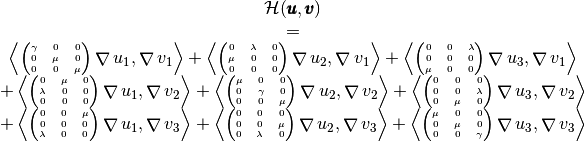
where
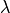 and
and 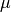 are the Lame coefficients and
are the Lame coefficients and 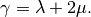
For example, we can explicitly compute the first two terms in the first column of
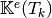 which are given by
which are given by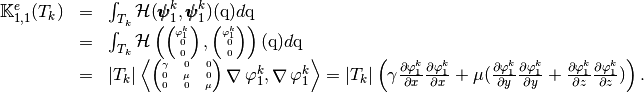
and
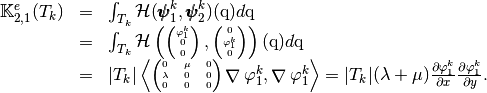
Using vectorized algorithm function
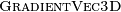 given in Algorithm 26, we obtain
the vectorized algorithm 29 for
given in Algorithm 26, we obtain
the vectorized algorithm 29 for 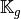 computation for the Elastic Stiffness matrix in 3d.
computation for the Elastic Stiffness matrix in 3d.Algorithm 29
Note
- pyOptFEM.FEM3D.elemMatrixVec.ElemStiffElasMatBa3DP1Vec(nme, q, me, volumes, la, mu)[source]
Computes all the element elastic stiffness matrices
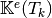 for
for 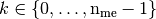 in local alternate basis.
in local alternate basis.Parameters: Returns: a (144*nme,) numpy array of floats.
We define on
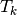 the local block basis
the local block basis 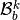 by
by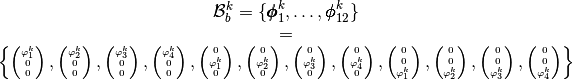
where
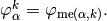
For example, using formula (?), we can explicitly compute the first two terms in the first column of
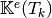 which are given by
which are given by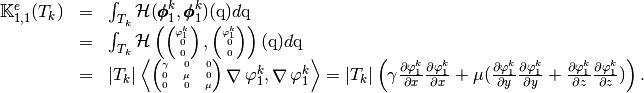
and
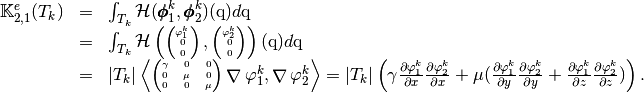
Using vectorized algorithm function
 given in Algorithm 26, we obtain
the vectorized algorithm 30 for
given in Algorithm 26, we obtain
the vectorized algorithm 30 for 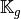 computation for the Elastic Stiffness matrix in 3d.
computation for the Elastic Stiffness matrix in 3d.Algorithm 30
Note
- pyOptFEM.FEM3D.elemMatrixVec.ElemStiffElasMatBb3DP1Vec(nme, q, me, volumes, L, M)[source]
Compute all the element elastic stiffness matrices,
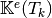 for
for 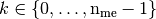 in local block basis.
in local block basis.Parameters: Returns: a (144*nme,) numpy array of floats.
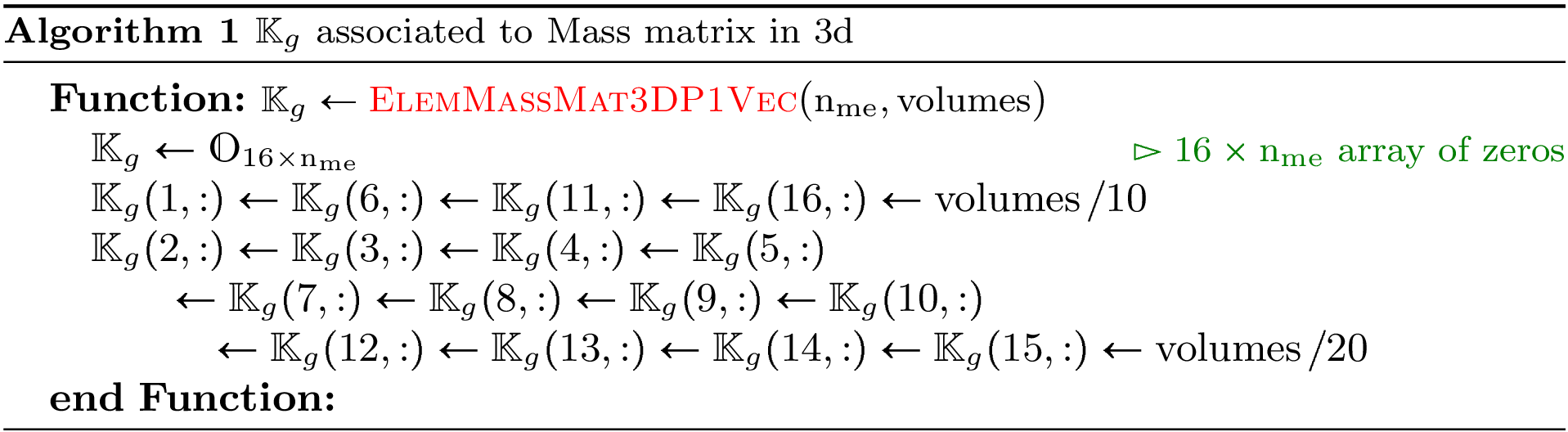


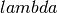 Lame parameter,
Lame parameter,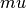 Lame parameter.
Lame parameter.
