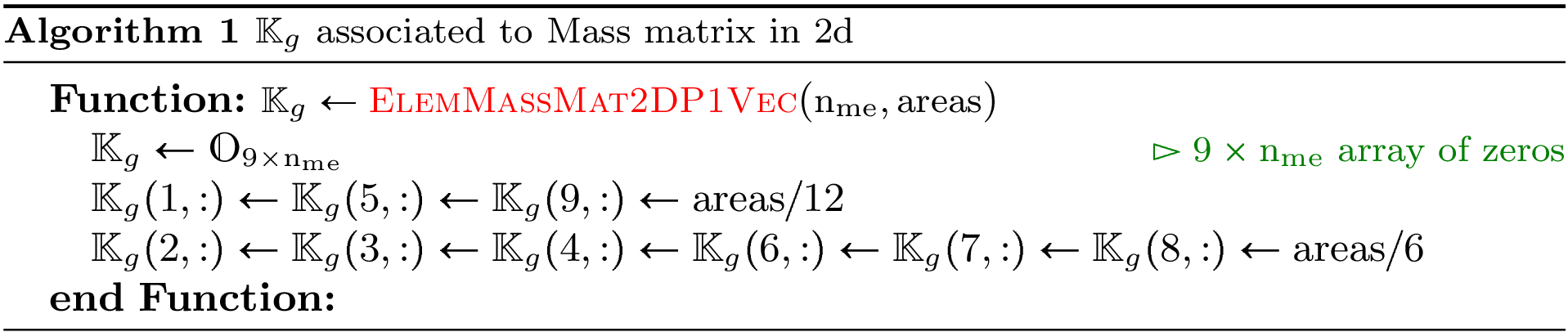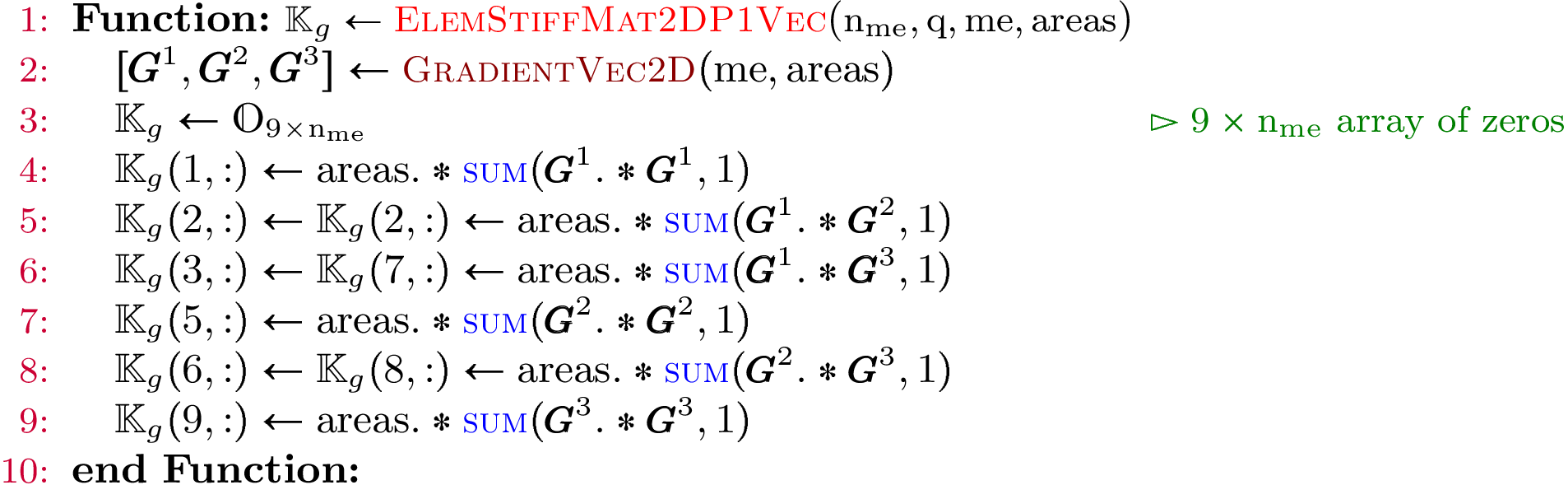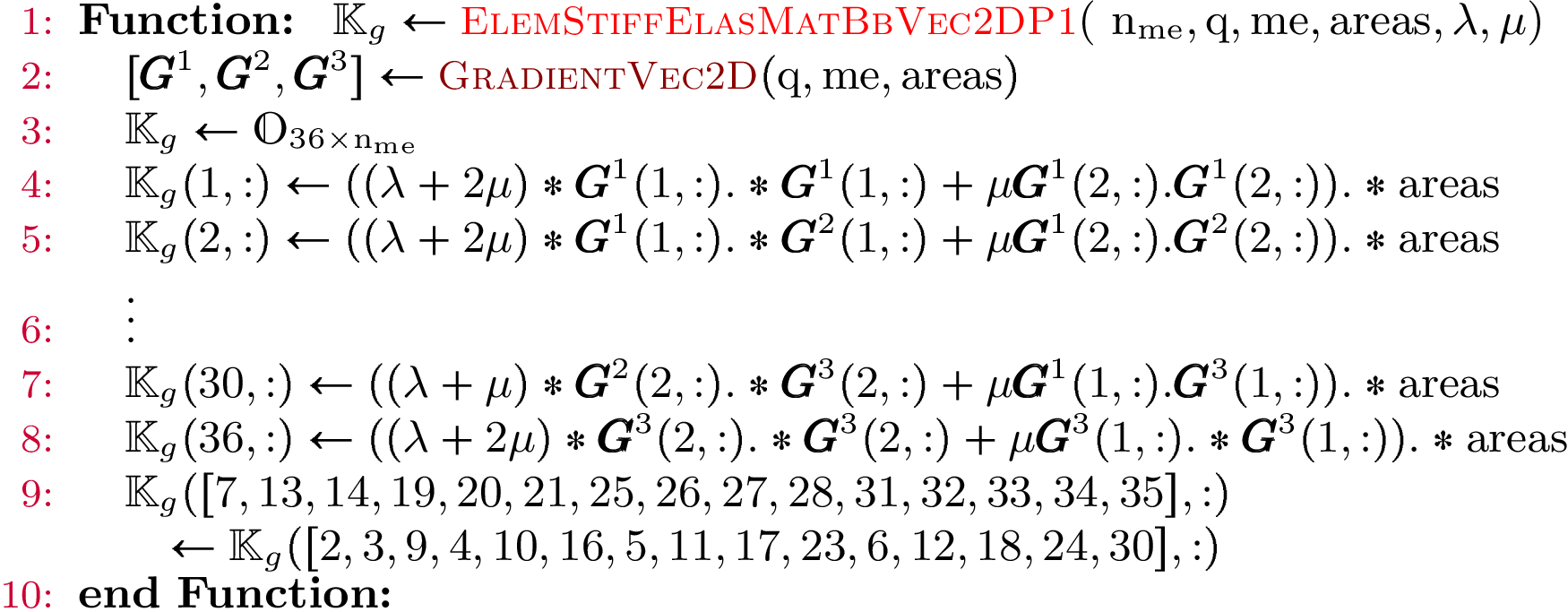Element Mass Matrix¶
We have
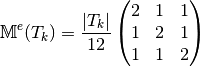
Then with 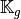 definition (see Section New Optimized assembling algorithm (version OptV2)) , we obtain
definition (see Section New Optimized assembling algorithm (version OptV2)) , we obtain
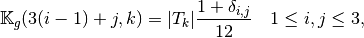
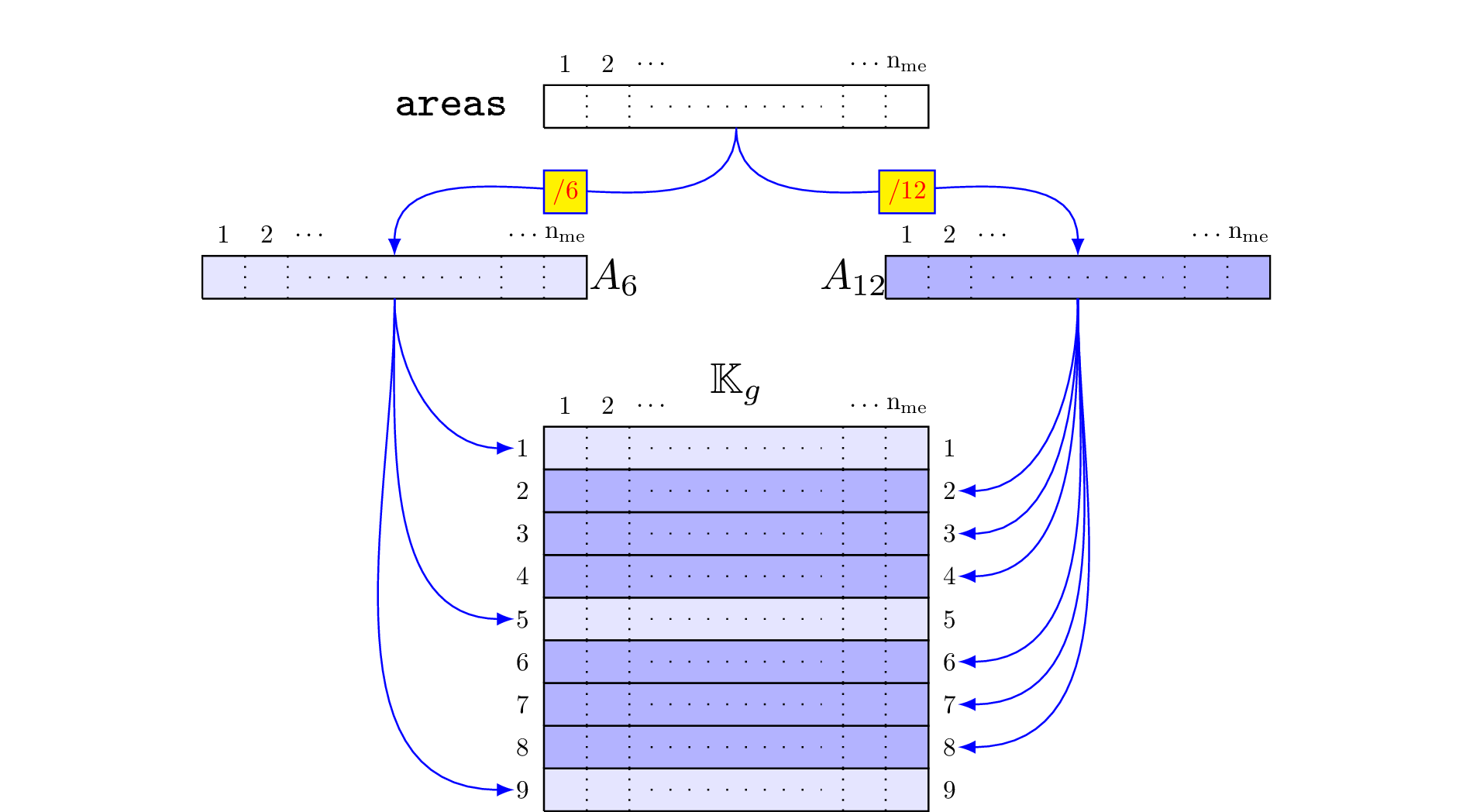
We represent in figure 135 the corresponding row-wise operations.
So the vectorized algorithm for 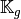 computation is simple and given in Algorithm 136.
computation is simple and given in Algorithm 136.
Algorithm 136
Note
- pyOptFEM.FEM2D.elemMatrixVec.ElemMassMat2DP1Vec(areas)[source]
Compute all the elementaries Mass matrices,
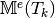 for
for 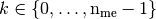
Parameters: areas ( 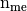 numpy array of floats) – areas of all the mesh elements.
numpy array of floats) – areas of all the mesh elements.Returns: a one dimensional numpy array of size 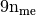
Element Stiffness Matrix¶
We have 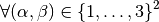
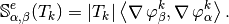
Using vectorized algorithm function 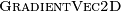 given in Algorithm 134, we obtain
the vectorized algorithm 137 for
given in Algorithm 134, we obtain
the vectorized algorithm 137 for 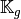 computation of the Stiffness matrix in 2d.
computation of the Stiffness matrix in 2d.
Algorithm 137
Note
- pyOptFEM.FEM2D.elemMatrixVec.ElemStiffMat2DP1Vec(nme, q, me, areas)[source]
Compute all the elementaries Stiff matrices,
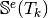 for
for 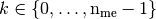
Parameters: - nme (int) – number of mesh elements,
- q (
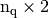 numpy array of floats) – mesh vertices,
numpy array of floats) – mesh vertices, - me (
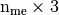 numpy array of integers) – mesh connectivity,
numpy array of integers) – mesh connectivity, - areas (
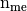 numpy array of floats) – areas of all the mesh elements.
numpy array of floats) – areas of all the mesh elements.
Returns: a one dimensional numpy array of size
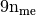
Element Stiffness Elasticity Matrix¶
We define on
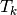 the local alternate basis
the local alternate basis 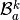 by
by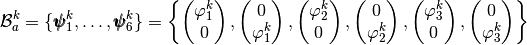
where
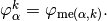 With notations of Presentation, we have
With notations of Presentation, we have
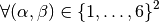
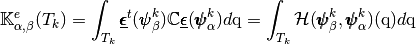
with,
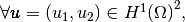
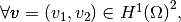
(1)
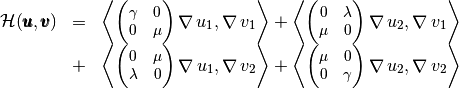
For example, we can compute explicitely the first two terms in the first column of
 which are given by
which are given by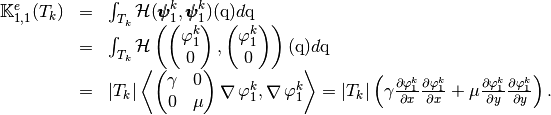
and
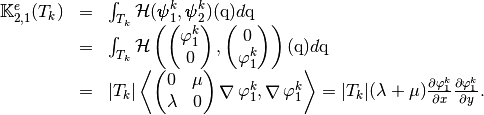
Using vectorized algorithm function
 given in Algorithm 134, we obtain
the vectorized algorithm 137 for
given in Algorithm 134, we obtain
the vectorized algorithm 137 for  computation of the Elasticity Stiffness matrix in 2d.
computation of the Elasticity Stiffness matrix in 2d.Algorithm 138
Note
- pyOptFEM.FEM2D.elemMatrixVec.ElemStiffElasMatBaVec2DP1(nme, q, me, areas, L, M)[source]
Compute all the elementaries Stiffness elasticity matrices,
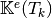 for
for 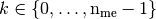 in local alternate basis.
in local alternate basis.Parameters: - nme (int) – number of mesh elements,
- q ((2,nq) numpy array of floats) – mesh vertices,
- me ((3,nme) numpy array of integers) – mesh connectivity,
- areas ((nme,) numpy array of floats) – areas of all the mesh elements.
- L – the
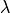 Lame parameter,
Lame parameter, - L – the
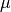 Lame parameter.
Lame parameter.
Returns: a (36*nme,) numpy array of floats.
We define on
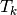 the local block basis
the local block basis 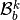 by
by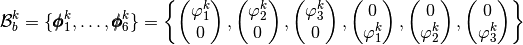
where
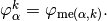
For example, using formula (1), we can explicitly compute the first two terms in the first column of
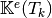 which are given by
which are given by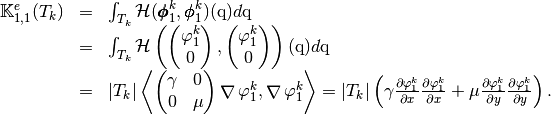
and
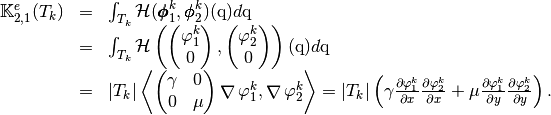
Using vectorized algorithm function
 given in Algorithm 134, we obtain
the vectorized algorithm 139 for
given in Algorithm 134, we obtain
the vectorized algorithm 139 for 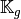 computation of the Elasticity Stiffness matrix in 2d.
computation of the Elasticity Stiffness matrix in 2d.Algorithm 139
Note
- pyOptFEM.FEM2D.elemMatrixVec.ElemStiffElasMatBbVec2DP1(nme, q, me, areas, L, M)[source]
Compute all the elementaries Stiffness elasticity matrices,
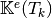 for
for 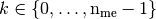 in local block basis.
in local block basis.Parameters: - nme (int) – number of mesh elements,
- q ((2,nq) numpy array of floats) – mesh vertices,
- me ((3,nme) numpy array of integers) – mesh connectivity,
- areas ((nme,) numpy array of floats) – areas of all the mesh elements.
- L – the
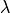 Lame parameter,
Lame parameter, - L – the
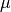 Lame parameter.
Lame parameter.
Returns: a (36*nme,) numpy array of floats.